10 Examples of Array Data Structure in Java
- The Tech Platform
- Nov 24, 2020
- 9 min read
Here are some of the important properties of the array in Java:
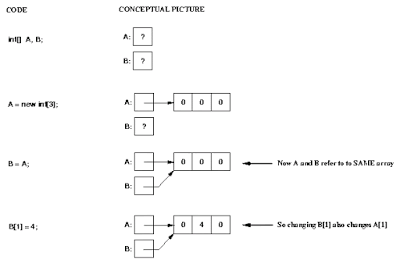
Unlike C and C++ array is an object in Java.
The length attribute of the array gives the length of an array, this is different from the length() method of String.
The length of an array is fixed and cannot be changed once created. The only way to increase or decrease length is to create a new array and copy the contents of an old array to a new array.
You can access elements of an array using the index, which is non-negative integer value e.g. a[1] will give you second element.
Array index starts at zero and ranges till length -1.
Unlike C and C++ Java performs bound checks while accessing array elements. Trying to access an invalid index in the array will throw java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
An array is typed in Java, you cannot store Integer in an array of String in Java. It will throw ArrayStoreException at runtime.
You can create an array of both primitive and reference types in Java.
Array elements are stored in the contiguous memory location, hence creating a big array of JVM may throw java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space if that big chunk of memory is not available.
The array is the backbone of many useful collection classes in Java e.g. ArrayList and HashMap both are backed by an array.
Now, let's see some examples of using an array in Java:
1) How to initialize an array in Java?
There are multiple ways to initialize an array in Java. You can only declare them or initialize them inline as shown below:
int[] primes = new int[10]; // elements will be initialize with default valueint[] even = new int[]{2, 4, 6, 8}; // inline initializationint[] odd = {1, 3, 5};Similarly, you can declare and initialize a two-dimensional array in Java. There are several ways to do so as I have shown in my articles about how to initialize a two-dimensional array in Java. Read that if you want to learn more about different ways to initialize a 2D array in Java.
2) How to get an element from the array?
You can retrieve an element of the array using index e.g. primes[0] will return the first element from prime array, primes[1] will return second element and primes[primes.length - 1] will return the last element from the array.
Just remember that index must be a non-negative integer value and starts with zero and ends with length - 1, trying to access an invalid index will throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExcepiton in Java.
Btw, if you are a complete beginner on data structure and algorithms then you can also refer a good course on to learn essential data structures like Algorithms and Data Structures - Part 1 and 2 courses on Pluralsight is a nice course to learn algorithms and Fundamental data structure.
Btw, you would need a Pluralsight membership to access this course which costs around $29 per month or $299 per year. I have that and I advise all programmers to join Pluralsight because it's very important to upgrade your skills. Even if you don't have a membership, don't worry, you can still access this course by taking their 10-day free pass which provides 200 minutes of free access to all of their 5000+ courses.
3) How to loop over an array in Java?
There are multiple ways to loop over an array in Java , but here are two of the most common ways to iterate or loop over an array in Java:
i) classic for loop
ii) enhanced for loop
Here is the sample program:
int[] primes = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11};
// looping over array using for loop
for(int i =0; i< primes.length; i++)
{
System.out.printf("element at index %d is %d %n", i, primes[i]);
}
// iterating over array using enhanced for loop
for(int prime : primes){
System.out.println("current number is " + prime);
}
Output
element at index 0 is 2
element at index 1 is 3
element at index 2 is 5
element at index 3 is 7
element at index 4 is 11
current number is 2
current number is 3
current number is 5
current number is 7
current number is 11There are both advantages and disadvantages to each of the approach. You must be careful with end condition while using for loop e.g. a condition <= length is a common cause of java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, and you don't have to worry about bounds when you use enhanced for loop for iterating over an array.
Similarly, when you use enhanced for loop, you don't have access to the current index so you cannot implement an algorithm that requires index like reversing array in place.
4) How to Sort an Array in Java?
There are two ways to sort an array in Java e.g. first use the library method Array.sort() which is also the preferred approach or write your own method to sort an array using quicksort or any sorting algorithm of your choice.
Apart from the interview, you should always use Arrays.sort() method for sorting an array in Java. This method allows you to sort an array in both ascending and descending order of elements as shown below:
int[] primes = {2, 17, 5, 23, 11};
System.out.println("array before sorting : " + Arrays.toString(primes));
System.out.println("sorting array in ascending order");
Arrays.sort(primes);
System.out.println("array after sorting : " + Arrays.toString(primes));
String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange", "grapes"};
System.out.println("String array before sorting : " + Arrays.toString(fruits));
System.out.println("Sorting array in descending order");
// only work with object arrays, not with // primitive arrays
Arrays.sort(fruits, Collections.reverseOrder());
System.out.println("array after sorting : " + Arrays.toString(fruits));
Output
array before sorting : [2, 17, 5, 23, 11]
sorting array in ascending order
array after sorting : [2, 5, 11, 17, 23]
String array before sorting : [apple, banana, orange, grapes]
Sorting array in descending order
array after sorting : [orange, grapes, banana, apple]The Arrays.sort() method allows only increasing order sorting for primitives but both normal and reverse order sorting for object arrays. In order to sort the primitive array in descending order, just sort the array in increasing order and reverse the array in place as shown here.
5) How to print an array in Java?
Even though the array is an object in Java, unfortunately, it doesn't override the toString() method, which means directly printing array as System.out.println(array) will not print its content instead it will print something which is not very helpful as shown below:
String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange", "grapes"};
System.out.println(fruits);
[Ljava.lang.String;@33909752It actually prints the type of array and then the hashcode in hexadecimal. Since most of the time we want to print elements of an array, this is not going to work, instead, we need to use Arrays.toString() method which prints the elements as shown below:
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fruits));
[orange, grapes, banana, apple]Btw, things are a little bit tricky with a two-dimensional array in Java. If you directly pass the 2D array to Arrays.toString() method then it will not print the content as shown below:
int[][] cubes = {
{1, 1},
{2, 4},
{3, 9},
{4, 16}
};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cubes));
Output
[[I@33909752The right way to print a two-dimensional array is to use the deepToString() method as shown below:
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(cubes));
Output
[[1, 1], [2, 4], [3, 9], [4, 16]]So, use Arrays.toString() method to print one dimensional array and Arrays.deepToString() method to print two or multi-dimensional array in Java. If you are interested to learn more about different types of array, I suggest checking out this Free Data Structure and Algorithm Courses which covers not only an array but other essential data structure as well.
6) How to check if two arrays are equal in Java?
What do you think? What should have been the natural way to check if two arrays are equal or not? well, it could have been by using the == operator, but unfortunately, Java doesn't support operator overloading.
It doesn't even have the equals() method, so you cannot even do like array.equals(other). So, how do you we check if two arrays are equal or not? Well, you can use Arrays.equals() and Arrays.deepEquals() to check if two arrays are equal or not.
Two arrays are said to be equal if they are of the same type, have the same length and have the same element at the corresponding index.
Here is an example of comparing two arrays in Java:
int[] primes = {3, 5, 7};
int[] odds = {3, 5, 7};
boolean isEqual = Arrays.equals(primes, odds);
if (isEqual) {
System.out.printf("array %s and %s are equal %n",
Arrays.toString(primes),
Arrays.toString(odds));
} else {
System.out.printf("array %s and %s are not equal %n",
Arrays.toString(primes),
Arrays.toString(odds));
}
Output
array [3, 5, 7] and [3, 5, 7] are equal
Similarly, you can use Arrays.deepToEquals() method to compare two-dimensional arrays in Java as shown in this example here.
7) How to convert an Array to String in Java?
You can convert an array to String like a comma-separated String by writing some utility method as shown below. This method accepts a String array and a delimiter and returns a big String where array elements are separated by a given delimiter.
You can use this method to convert a string array to comma separated String, people separated string or colon-separated String in Java. Btw, This is also our 7th example of an array in Java.
/*** Java method to convert an array to String delimited by given delimiter
*
* @param array
* @param delimiter
* @return String where array elements separated by delimiter
*/public static String arrayToString(String[] array, String delimiter) {
String result = "";
if (array.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s : array) {
sb.append(s).append(delimiter);
}
result = sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1).toString();
}
return result;
}Here is the result of some testing, where we have used this method to convert an array to CSV and colon-delimited String in Java
String[] currencies = {"USD", "INR", "AUD", "GBP"};
System.out.println("array is : " + Arrays.toString(currencies));
// array to comma separated StringString output = arrayToString(currencies, ",");
System.out.println("CSV string: " + output);
// array to colon separated String
output = arrayToString(currencies, ":");
System.out.println("colon string: " + output);
Output
array is : [USD, INR, AUD, GBP]
CSV string: USD,INR,AUD,GBP
colon string: USD:INR:AUD:GBPYou can see that our String contains all the elements from the array and they are also separated by comma and colon. Btw, If you are preparing for a coding interview, then I suggest you join Data Structure and Algorithms - Interview!! course on Udemy, it's a great course to learn about essential data structure and prepare for interviews.
8) How to convert an Array to ArrayList in Java?
There are multiple ways to convert an Array to ArrayList in Java, as shown in this article, but I'll share the easiest way to do that. Yes, you guessed it right, I'll use the Arrays.asList() method to convert an Array to ArrayList in Java as shown below:
String[] hosting = {"Bluehost", "GoDaddy", "Google"};
List<String> listOfHosting = Arrays.asList(hosting);Remember, the task is not completed yet as most of the developers will think. We have got a List, not the ArrayList, also the list we have is a read-only list where you cannot add or remove elements but you can replace elements with valid indices.
In order to convert it to our general-purpose ArrayList, we need to use the copy constructor provided by Collection class as shown in the following example:
ArrayList<String> hostingCompanies = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(hosting));This is the right way to convert an Array to ArrayList in Java.
It is also used to declare ArrayList with values because you can replace the array with values anytime, as shown below:
ArrayList<String> hostingCompanies = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("Sony",
"Apple", "Amazon"));9) How to do a binary search in Java?
There are two ways to do a binary search in Java either write your own method as shown here or use the Arrays.binarySearch() method, which accepts an array and the element you want to search and return its index if the element is found or -1 otherwise.
Btw, If you are preparing for a coding interview, then I suggest you join Data Structures in Java: An Interview Refreshercourse on Educative, it's a great course to learn about essential data structure and prepare for interviews.
10) How to create a subarray from an array?
You can use the System.arrayCopy() method to create a subarray from an array in Java. This method is very flexible it allows you to specify start index and how many elements from the start index, this way you can copy any number of elements from an index from the array in Java.
Here is an example of creating a sub-array in Java:
String[] bestIndianCreditCards = {"ICICI Instant Platinum Credit Card",
"Standard Chartered Platinum Rewards Credit Card",
"Citibank Platinum Credit Card",
"SBI Gold Credit Card",
"Yatra SBI Credit Card",
"HDFC Platinum Plus Credit Card",
"HDFC Solitaire Credit Card"};
// let's create sub array in JavaString[] sbiCards = new String[2];
System.arraycopy(bestIndianCreditCards, 3, sbiCards, 0, 2);
System.out.println("original array: " + Arrays.toString(bestIndianCreditCards));
System.out.println("copy of array: " + Arrays.toString(sbiCards));
Output
original array: [ICICI Instant Platinum Credit Card,
Standard Chartered Platinum Rewards Credit Card, Citibank Platinum Credit Card,
SBI Gold Credit Card, Yatra SBI Credit Card, HDFC Platinum Plus Credit Card,
HDFC Solitaire Credit Card]
copy of array: [SBI Gold Credit Card, Yatra SBI Credit Card]You can see we have easily extracted only SBI credit cards from the big list of credit card array. Since we specified the source position as 3, System.arrayCopy() started copying elements from the 3rd index or fourth element and then copied it into destination array starting from position zero. The last element is for how many elements to copy, we copied only two because there were only two SBI credit card in the list.
Source: java67

Comments