Dart
- The Tech Platform
- Apr 9, 2021
- 5 min read
Dart is an open-source general-purpose programming language. It is originally developed by Google and later approved as a standard by ECMA. Dart is a new programming language meant for the server as well as the browser. Introduced by Google, the Dart SDK ships with its compiler – the Dart VM. The SDK also includes a utility -dart2js, a transpiler that generates JavaScript equivalent of a Dart Script. This tutorial provides a basic level understanding of the Dart programming language.
The following example shows simple Dart programming.
void main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
print('hello ${i + 1}');
}
} Data Type
Dart is a Strongly Typed programming language. It means, each value you use in your programming language has a type either string or number and must be known when the code is compiled. Here, we are going to discuss the most common basic data types used in the Dart programming language.
Variables and Functions
Variables are the namespace in memory that stores values. The name of a variable is called as identifiers. They are the data containers, which can store the value of any type. For example:
var myAge = 50; Here, myAge is a variable that stores an integer value 50. We can also give it int and double. However, Dart has a feature Type Inference, which infers the types of values. So, if you create a variable with a var keyword, Dart can infer that variable as of type integer.
Besides variable, Functions are another core feature of any programming language. Functions are a set of statements that performs a specific task. They are organized into the logical blocks of code that are readable, maintainable, and reusable. The function declaration contains the function name, return type, and parameters. The following example explains the function used in Dart programming.
//Function declaration
num addNumbers(num a, num b) {
// Here, we use num as a type because it should work with int and double both.
return a + b;
}
var price1 = 29.99;
var price2 = 20.81;
var total = addNumbers(price1, price2);
var num1 = 10;
var num2 = 45;
var total2 = addNumbers(num1, num2); Operators
Dart language supports all operators, as you are familiar with other programming languages such as C, Kotlin, and Swift. The operator's name is listed below:
Arithmetic
Equality
Increment and Decrement
Logical
Comparison
Decision Making and Loops
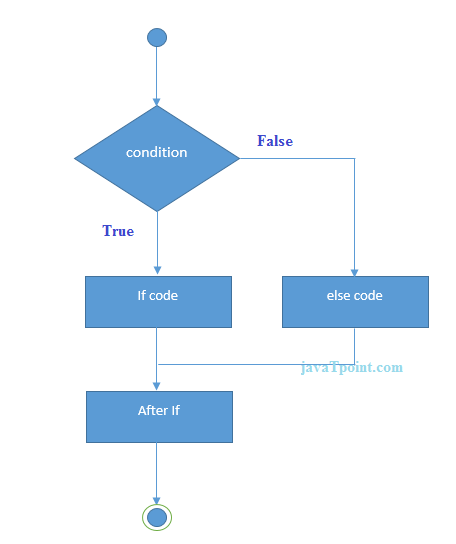
The decision-making is a feature that allows you to evaluate a condition before the instructions are executed. The Dart language supports the following types of decision-making statements:
If statement
If-else statement
Switch statement
The below diagram explains it more clearly.
Example
void main() {
var num = 12;
if (num % 2 = = 0) {
print("Number is Even.");
} else {
print("Number is Odd.");
}
} Loops are used to execute a block of code repeatedly until a specified condition becomes true. Dart language supports the following types of loop statements:
for
for..in
while
do..while
The below diagram explains it more clearly.
Example
void main() {
var name = ["Peter", "Rinky Ponting", "Abhishek"];
for (var prop in name) {
print(prop);
}
} Comments
Comments are the lines of non-executable code. They are one of the main aspects of all programming languages. The purpose of this is to provide information about the project, variable, or an operation. There are three types of comments in Dart programming:
Make format comments: It is a single line comment (//)
Block Comments: It is a multi-line comment (/*...*/)
Doc Comments: It is a document comment that used for member and types (///)
Continue and Break
Dart has also used the continue and break keyword in the loop, and elsewhere it required. The continue statement allows you to skip the remaining code inside the loop and immediately jump to the next iteration of the loop. We can understand it from the following example.
Example
void main() {
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
print("Hello");
continue; //it will skip the rest statement
}
print(i);
}
} The break statement allows you to terminate or stops the current flow of a program and continues execution after the body of the loop. The following example gives a detailed explanation.
Example
void main() {
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
print("Hello");
break;//it will terminate the rest statement
}
print(i);
}
} Final and Const Keyword
We can use a final keyword to restrict the user. It can be applied in many contexts, such as variables, classes, and methods.
Const keyword is used to declare constant. We cannot change the value of the const keyword after assigning it.
Example
void main() {
final a = 100;
const pi = 3.14;
print(a);
print(pi);
} Object-Oriented Programming
Dart is an object-oriented programming language, which means every value in a Dart is an object. A number is also an object in Dart language. Dart programming supports the concept of OOPs features like objects, classes, interfaces, etc.
Object: An object is an entity, which has state and behavior. It can be physical or logical. In Dart, every value is an object, even primitive values like text and number. Dart can also allow you to build your custom object to express more complex relations between data.
Class: A class is a collection of objects. It means the objects are created with the help of classes because every object needs a blueprint based on which you can create an individual object. A class definition includes the following things:
Fields
Methods
Constructor
Getters and setters
Let us see an example, which helps you to understand the OOPs concept easily.
class Mobile {
// Property Declaration
String color, brandName, modelName;
// Method Creation
String calling() {
return "Mobile can do call to everyone.";
}
String musicPlay() {
return "Mobile can play all types of Music.";
}
String clickPicture() {
return "Mobile can take pictures.";
}
}
void main() {
// Object Creation
var myMob = new Mobile();
// Accessing Class's Property
myMob.color = "Black";
myMob.brandName = "Apple Inc.";
myMob.modelName = "iPhone 11 Pro";
//Display Output
print(myMob.color);
print(myMob.modelName);
print(myMob.brandName);
print(myMob.calling());
print(myMob.musicPlay());
print(myMob.clickPicture());
} In the above example, we define a class Mobile, which has three variables of string type and three functions or methods. Then, we create a main function which Dart will execute first when your app starts. Inside the main, we create an object to access the class's properties. Finally, we print the output.
Features:
Dart is an open-source programming language, which means it is freely available.
Dart supports all primary operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Macintosh, etc. The Dart has its own Virtual Machine which known as Dart VM, that allows us to run the Dart code in every operating system.
Dart is an object-oriented programming language and supports all oops concepts such as classes, inheritance, interfaces and optional typing features.
Dart is an asynchronous programming language, which means it supports multithreading using Isolates.
Dart provides the flexibility to compile the code and fast as well
The Dart is the type safe language, which means it uses both static type checking and runtime checks to confirm that a variable's value always matches the variable's static type, sometimes it known as the sound typing.
The Dart treats everything as an object. The value which assigns to the variable is an object. The functions, numbers, and strings are also an object in Dart. All objects inherit from Object class.
Source: javapoint
The Tech Platform







Comments