In today's data-driven world, organizations collect and process vast amounts of personal information. With this increased reliance on data comes a growing responsibility to protect individual privacy. Data Privacy Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are a crucial tool for organizations to navigate this responsibility.
This article dives into the essentials of DPIAs, unpacking their purpose, when required, and the key steps involved in conducting one. By understanding DPIAs, organizations can ensure they handle personal data responsibly, comply with regulations, and foster trust with data subjects.
What is DIPA?
A Data Privacy Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a systematic process used to identify and minimize the risks of processing personal data. It is an essential assessment tool that helps organizations to understand the potential impact their activities have on individual privacy.
Think of a DPIA as a blueprint for ensuring the privacy of individuals' data throughout its processing lifecycle. By proactively identifying risks and steps to mitigate them, organizations can avoid potential issues and demonstrate their commitment to data protection.
Importance of DPIAs in data privacy compliance
DPIAs (Data Privacy Impact Assessments) are crucial for organizations that handle personal data because they achieve data privacy compliance.
Here's why they're so important:
Proactive Approach: Unlike reactive measures taken after a data breach, DPIAs encourage a proactive approach. By identifying and addressing privacy risks at the planning stage of a project, organizations can prevent issues before they happen. This saves time, and resources, and avoids the reputational damage that can follow a privacy breach.
Reduced Risk: DPIAs help pinpoint areas where personal data might be vulnerable. This allows organizations to implement appropriate safeguards encryption, access controls, and data minimization practices. Organizations ensure they can handle data responsibly and comply with regulations by mitigating these risks.
Demonstrated Accountability: Data privacy regulations like GDPR emphasize accountability. Conducting DPIAs demonstrates to regulators and data subjects that an organization takes data privacy seriously. The documented assessment process is evidence of due diligence and a commitment to responsible data handling.
Improved Compliance: By systematically analyzing data processing activities, DPIAs help organizations identify areas where their practices might not align with regulations. This allows them to adjust their procedures to ensure compliance and avoid potential fines or penalties.
Building Trust: In today's data-driven world, consumers are increasingly concerned about how their personal information is used. By conducting DPIAs, organizations can show their commitment to data protection and build trust with their customers. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and brand reputation.
In short, DPIAs are tools for organizations to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of data privacy regulations. They promote proactive compliance, minimize risks, and demonstrate accountability, ultimately fostering trust with regulators and data subjects.

When is a DPIA Required?
Data protection regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, mandate DPIAs for specific high-risk processing activities. These scenarios involve individuals' privacy rights and require a thorough assessment before implementation. Here are the key mandatory triggers:
Systematic and Extensive Profiling: This refers to the automated processing of personal data to analyze or predict a person's behavior, preferences, characteristics, or future outcomes. If this profiling is done on a large scale (affecting a significant number of individuals) and has a significant effect (e.g., influencing their access to opportunities or services), a DPIA is mandatory. For instance, using extensive profiling data to deny loan applications would necessitate a DPIA.
Large-Scale Processing of Special Categories of Data: Special categories of data, as defined in the GDPR, are sensitive and reveal information about a person's racial or ethnic origin, political opinions, religious beliefs, trade union membership, health data, genetic data, biometric data for identification purposes, sex life, or sexual orientation. Processing large amounts of this data type carries a high inherent risk, so a DPIA evaluates the potential impact and implements appropriate safeguards.
Public Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of publicly accessible areas (e.g., extensive CCTV camera networks in a city) can have a chilling effect on people's privacy. If the monitoring is conducted on a large scale, a DPIA is necessary to assess the impact on individuals and ensure appropriate safeguards are in place.
Additional Considerations for High-Risk Processing:
While not mandatory triggers, these factors indicate situations where a DPIA might be highly advisable:
Innovative Technology: Using new or emerging technologies for data processing can introduce unforeseen risks to privacy. A DPIA can help identify and mitigate these by comprehensively examining the technology's potential impact on data handling. For instance, a DPIA would be beneficial when implementing facial recognition systems in public spaces.
Data Matching or Combining Datasets: When data from different sources is combined (e.g., combining customer purchase history with social media data), the privacy risks can be amplified. A DPIA can assess the overall impact on individuals and ensure the combined data is used responsibly.
Data Subject Rights: If a processing activity makes it difficult for individuals to exercise their data subject rights under regulations (e.g., the right to access, rectify, or erase their data), a DPIA might be needed. The assessment can help identify potential obstacles and ensure these rights are respected throughout the processing lifecycle.
Remember
Even if a DPIA isn't mandatory, conducting one for any high-risk data processing activity demonstrates a proactive approach to data privacy and helps organizations ensure compliance with regulations. It's a valuable tool for mitigating risks and fostering trust with regulators and data subjects.
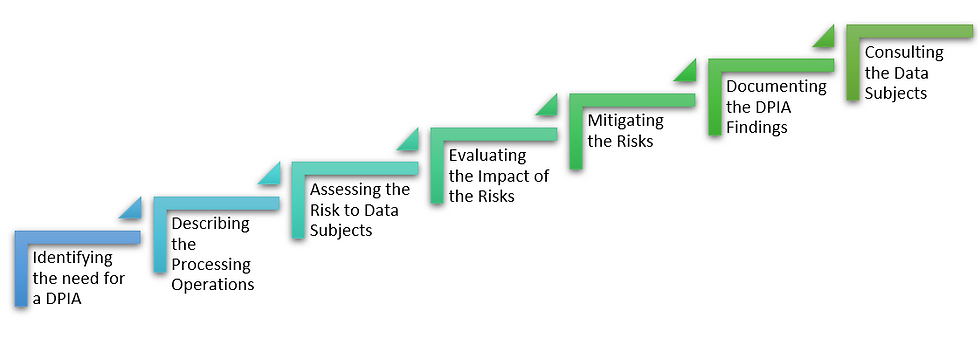
Conducting a DPIA
A Data Privacy Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a structured process that helps organizations identify and minimize risks associated with processing personal data. The specific steps may vary slightly depending on the regulations you're subject to, but here are the key phases involved:
1. Identifying the Need for a DPIA:
The first step determines if a DPIA is mandatory for your planned processing activity. Regulations like GDPR outline specific scenarios that trigger the DPIA (covered previously) requirement. Additionally, consider the factors mentioned earlier (innovative technology, data matching, etc.) to assess if a DPIA is advisable even if not strictly mandated.
2. Describing the Processing Operation:
Clearly define the data processing activity you're planning. This includes details like:
What personal data will be collected?
What is the purpose of collecting and processing this data?
How will the data be processed (e.g., storage, analysis)?
Who will have access to the data?
How long will the data be retained?
3. Assessing the Risks to Data Subjects:
Identify the potential risks to individuals whose data is being processed. Consider factors like:
Can the data be used to discriminate against individuals?
Is there a risk of data breaches or unauthorized access?
Could the processing cause individuals psychological harm or reputational damage?
4. Evaluating the Impact of the Risks:
Once the risks are identified, assess the severity of each risk. Consider the likelihood of the risk occurring and the potential consequences for individuals. This helps prioritize which risks need the most attention.
5. Mitigating the Risks (Controls and Safeguards):
Develop strategies to minimize the identified risks. This might involve implementing technical or organizational controls, such as:
Encryption to protect data at rest and in transit
Access controls to restrict who can access the data
Data minimization practices to only collect and store the necessary data
Regular security audits and training for personnel
6. Documenting the DPIA Findings:
Document the entire DPIA process, including the identified risks, the implemented safeguards, and the rationale behind your decisions. This documented assessment of your due diligence helps demonstrate compliance with regulations.
7. Consulting with Data Subjects (Where Appropriate):
In some cases, regulations may require consulting with data subjects before implementing a high-risk processing activity. This consultation allows individuals to understand how their data will be used and provide feedback on the potential impact.
Benefits of DPIAs
Here's why DPIA are valuable tools for organizations:
1. Proactive Approach to Data Privacy Compliance:
DPIAs encourage a proactive approach to data privacy. By identifying and addressing potential privacy risks at the planning stage of a project, organizations can avoid issues before they happen. This saves time, and resources, and mitigates the potential for regulatory fines or penalties that can arise from non-compliance.
2. Identifying and Mitigating Data Privacy Risks:
A key benefit of DPIAs is their ability to pinpoint areas where personal data might be vulnerable. This allows organizations to implement appropriate safeguards such as encryption, access controls, and data minimization practices. By proactively mitigating these risks, organizations ensure they handle data responsibly and adhere to privacy regulations.
3. Demonstrating Accountability to Regulators and Data Subjects:
Data privacy regulations like GDPR emphasize accountability. Conducting DPIAs demonstrates to regulators and data subjects that an organization takes data privacy seriously. The documented assessment process is evidence of due diligence and a commitment to responsible data handling. This fosters trust and transparency, which can be crucial for maintaining a positive reputation.
In addition to these core benefits, DPIAs can also:
Increase Customer Trust: By demonstrating a commitment to data protection, DPIAs can help build customer trust, leading to increased customer loyalty.
Improve Efficiency: Conducting a DPIA can help identify and streamline data processing activities, potentially leading to increased efficiency.

Overall, DPIAs are a valuable tool for organizations of all sizes to navigate the evolving landscape of data privacy regulations. They promote proactive compliance, minimize risks, foster trust, and contribute to improved efficiency in data handling practices.
Conclusion
DPIAs are crucial for organizations handling personal data. They ensure compliance, proactively manage risks, show accountability, build trust, and potentially improve efficiency. Understanding DPIAs empowers organizations to navigate data privacy effectively.

canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188 canduan188