What are SuperCookies? Difference between Cookies and SuperCookies explained
- The Tech Platform

- Feb 16, 2021
- 4 min read
Updated: Jun 15, 2023
Supercookies pose a significant threat to online privacy as they can track your internet activities without being stored on your computer, making them difficult to detect and remove. Unlike the delicious edible cookies, we often hear about, computer cookies are small text files that store information about your online behavior.
One type of cookie, known as an HTTP cookie, is placed on your web browser by a website you visit. It contains data that allows the website to recognize you as a returning user when you revisit it. Now that we understand the basics of cookies, let's delve deeper into how they function and explore the concept of Supercookies.
What are Cookies?
When we visit websites, we often accept that they will download something called "Cookies" onto our computer systems. These cookies are small files that help make our web browsing faster and more convenient for future visits. While some cookies are harmless and improve our experience by storing information to reduce loading times on different pages, others can be a bit fishy.
Let's imagine you visited an online shopping website and added items to your cart but didn't make a purchase right away. When you return to the website a few days later, you'll notice that you're still logged in, and your cart still contains the items you added earlier. This is possible because the website stores your login status and cart details in a cookie file that it reads when you revisit the site. So, cookies can actually enhance your browsing and shopping experience.
It's important to know that not all cookies are designed to tamper with your online security; many are beneficial. There are different types of browser cookies, including:
HTTP-only cookies help in reducing a cookie’s vulnerability to cross-site scripting (XSS) attack
Flash cookies ( a type of supercookie )
Third-party cookies that originate from a third domain and are categorized as harmful
First-party cookies are also known as permanent cookies, they help sites to remember user’s information and settings when they revisit them in the future
Session cookies are best known as a website’s short time memory
Secure cookies that can only be transmitted over an encrypted connection
Zombie cookies are closely related to flash cookies and can instantly recreate themselves if someone deletes it
Some cookies are set to automatically delete after a certain period, called persistent cookies. However, there are also supercookies that are challenging to delete as they are designed to evade common methods of removal. Let's go deeper into the concept of supercookies to understand them better.
What are Supercookies?
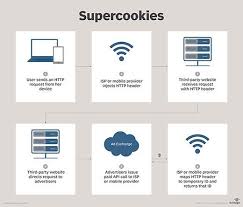
Unlike regular cookies, supercookies serve a more concerning purpose. They are a type of tracking cookie inserted into an HTTP header by an internet service provider (ISP) to gather data about a user's internet browsing history, habits, and preferences. Referred to as Unique Identifier Headers (UIDH), supercookies are not technically HTTP cookies. Instead, they are injected into packets transmitted between the user's device and the service they connect to. The ISP adds an extra HTTP header to the packets after they leave the user's computer when it detects the user's HTTP traffic.
Supercookies can collect a wide range of personal data related to a user's internet browsing habits and preferences, including the websites they visit and the times they visit them. It doesn't matter which browser the user is using or if they switch browsers—the supercookies persist. They can also access and gather information from traditional tracking cookies, such as login details, plug-in data, cached images, and files. Even if the user deletes the traditional cookie, the supercookie can still retain that information.
Are Supercookies a Threat to Privacy?
Regular cookies can be easily cleared or blocked to prevent tracking, but supercookies are much more persistent and difficult to get rid of. Unlike traditional cookies, supercookies are not stored in your browser and can't be removed by clearing browsing data. They are injected by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) between your device and the server you're connecting to. This makes them harder to detect and eliminate, as they don't exist in typical cookie storage locations on your computer.
Supercookies, being tracking cookies, can gather sensitive information like login credentials, plug-in data, and cached images or files. They pose a significant privacy risk, as they are nearly impossible to remove through standard methods like clearing the browser cache or using adblockers. Users can only opt-out if their ISP allows it.
The Dangers of Supercookies
Supercookies have raised concerns over privacy breaches. Verizon, for example, faced a hefty fine for using supercookies to track user's web browsing activities without their knowledge. Unlike traditional cookies, which are tied to specific websites, supercookies can be shared with any website, exposing a wealth of user information and enabling the collection and resale of personal data.
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) warns that supercookies can be used by advertisers to recover deleted cookies from user devices and link them with new strategies, evading user prevention measures. Supercookies can also apply to data sent from applications, enabling comprehensive profiling of a user's internet usage habits.
How you can remove a Supercookie?
Removing supercookies is challenging, as they store extensive user information and may not be stored on the user's device. However, there are some measures you can take to mitigate their impact. Making encrypted connections with websites by visiting only HTTPS websites using TLS or SSL certificates can help avoid supercookies from tracking your activities. Additionally, redirecting internet traffic through a secure network, such as using a VPN, creates an encrypted connection between you and the rest of the internet.
Major browsers like Firefox, Chrome, Edge, and Safari are taking steps to crack down on supercookies, implementing stricter privacy measures.
Ultimately, using the best browser security tools, such as HTTPS and VPN, can enhance your online security. However, the ideal solution lies in strong regulations that require ISPs to allow users to reject programs that track their internet footprints, safeguarding privacy on a broader scale.
Difference: Cookies vs Supercookies
Factors | Cookies | Supercookies |
|---|---|---|
Type of Storage | Stored in the browser | Injected between device and server |
Persistence | Can be cleared or blocked | Difficult to remove or detect |
Tracking Ability | Limited to a single website | Can be shared with multiple websites |
Information | Contains basic user data | Can gather extensive user browsing habits |
Removal | Can be deleted by the user | Not easily removed through standard methods |
Privacy Risk | Lower risk compared to supercookies | Higher risk due to extensive tracking |
Prevention | Can be blocked by browser settings | Adblockers and privacy trackers may not work |
Industry Response | Browsers implementing stricter privacy measures | Cracking down on supercookies |
Conclusion
Supercookies are a more intrusive form of tracking cookies that pose a significant threat to user privacy. While regular cookies are stored in the browser and can be easily cleared or blocked, supercookies are injected by ISPs between the user's device and the server they connect to. This makes them difficult to detect and remove, as they don't reside in typical cookie storage locations.




Comments