WordPress is a free, open-source website creation platform. On a more technical level, WordPress is a content management system (CMS) written in PHP that uses a MySQL database. In non-geek speak, WordPress is the easiest and most powerful blogging and website builder in existence today.
WordPress is an excellent website platform for a variety of websites. From blogging to e-commerce to business and portfolio websites, WordPress is a versatile CMS. Designed with usability and flexibility in mind, WordPress is a great solution for both large and small websites.
Types of Website with wordpress
Here are just a few examples of the types of websites you can build with WordPress:
Blog – A blog is a special type of website devoted to sharing thoughts, photos, reviews, tutorials, recipes and so much more. Blogs usually display the most recently-published content first.
E-commerce website – An e-commerce website allows you to sell goods or services online and collect payment via an online payment system. You can download and install a WordPress e-commerce plugin to extend the default functionality of WordPress so you can have an online store on your website.
Business website – Many businesses will benefit from having an online presence in the form of their own website. If your business needs a website for customers to learn about your company and what you have to offer, WordPress is an excellent option. Customers can contact you, ask for a quote, schedule an appointment and much more.
Membership website – A membership website allows you to put content behind a paywall or an account login. To access pages or posts, users must login or pay for the content. WordPress can also handle membership websites with additional plugins.
Portfolio website – Show off your artwork, design skills and more with a portfolio website built on WordPress.
Forum website – A forum website can be a helpful place for users to ask questions or share advice. Believe it or not, many forum websites run on WordPress.
Event website – Hosting an event? WordPress makes it easy for you to share your event details and sell tickets.
E-learning website – Students can take online courses, track their progress, download resources and much more from an e-learning website. With a special kind of plugin called a WordPress LMS plugin, you can offer online courses from a WordPress website.
Wedding website – Share the details of your big day with a wedding website built on WordPress. With an array of WordPress wedding themes, you can get a website up quickly and easily.
Writing Post
To write a post:
Log in to your WordPress Administration Screen (Dashboard).
Click the ‘Posts’ tab.
Click the ‘Add New’ sub-tab.
Start filling in the blanks: enter your post title in the upper field, and enter your post body content in the main post editing box below it.
As needed, select a category, add tags, and make other selections from the sections below the post. (Each of these sections is explained below.)
When you are ready, click Publish.
Screen Options:
There are more editing fields available to you than you see on first login. The Screen Options area allows you to choose which Post Fields are displayed or hidden from your editing area, which allows you to minimize clutter and customize according to your needs.
You’ll find the Screen Options tab at the very top of your screen, and if you click on it, you’ll see a list of available editing boxes that you can use. Check the box for each Post Field you want displayed, or uncheck the box to hide that module. Click the Screen Options tab again to close the tab.
Once you’ve customized how editing screen, your options are saved so you don’t have to select or hide them again next time you log in.
Post Field Descriptions:

1. Title/Headline Box
This box should contain the title of your post. You can use any phrase, words, or characters. (Avoid using the same title on more than one page.) You can use commas, apostrophes, quotes, hyphens/dashes, and other typical symbols in the post like “My Site – Here’s Lookin’ at You, Kid.” WordPress will then clean it up to generate a user-friendly and URL-valid name of the post (also called the “post slug”) to create the permalink for the post.
2. Permalink
Permalink stands for “permanent link.” That means a post URL that does not expose the post ID which could be subject to a change (e.g. when moving to different blogging system), but it rather contains a user-friendly post name derived from the post title which could also change, although not recommended, but in a more controllable way. This post name (also referred to as “post slug” or just “slug”) can be edited, depending on your Permalinks settings, using the “Edit” button. (To change your settings, go to Administration Screens > Settings > Permalinks). The permalink is automatically generated based on the title you set to the post and is shown below the title field. Punctuation such as commas, quotes, apostrophes, and invalid URL characters are removed and spaces are substituted with dashes to separate each word. If your title is “My Site – Here’s Lookin’ at You, Kid”, it will be cleaned up to create the slug “my-site-heres-lookin-at-you-kid”. You can manually change this, maybe shortening it to “my-site-lookin-at-you-kid”.
3. Body Copy Box
The blank box where you enter your writing, links, images, links to images, and any information you want to display on your site. You can use either the visual (WYSIWYG) editor or the text view to compose your posts. For more on the text view, see the section below, Visual Versus Text Editor.
4. Publish Box
Contains buttons that control the state of your post. The main states are Draft and Published. Draft means the post has not been published and remains in draft status for the post creator. A Published status means the post has been published and is live on your site.
Preview Button Allows you to view the post before publishing.
Save Draft Allows you to save your post as a draft rather than immediately publishing it. To return to your drafts later, visit Posts – Edit in the menu bar, then select your post from the list.
Status If you select a specific publish status (click Edit next to Status:Draft) and click the update post or “Publish” button, that status is applied to the post. For example, to save a post in the Pending Review status, select Pending Review from the Publish Status drop-down box, and click Save As Pending. (You will see all posts organized by status by going to Administration Screens > Posts > Edit).
Visibility This determines how your post appears to the world. (click Edit next to Visibility) Public posts will be visible by all website visitors once published. Password Protected posts are published to all, but visitors must know the password to view the post content. Private posts are visible only to you (and to other editors or admins within your site).
Revisions Click Browse to see all of the changes you’ve made to your post.
Scheduling To schedule a post for publication on a future time or date, click Edit next to the words “Publish immediately.” You can also change the publish date to a date in the past to back-date posts. Change the settings to the desired time and date. You must also click the Publish button when you have completed the post to publish at the desired time and date.
5. Format Box
Allows you to choose a format for a post. Styling and appearance are handled by the individual themes.
6. Categories Box
The general topic of the post. It is typical for a blog to have 7-10 categories for content. Readers can browse specific categories to see all posts in the category. You can manage your categories by going to Administration Screens > Posts > Categories.
7. Tags Box
These are micro-categories for the post, similar to including index entries for a page. Posts with similar tags are linked together when a user clicks one of the tags. Tags have to be enabled with the right code in your theme for them to appear in your post. Add new tags to the post by typing the tag into the box and clicking “Add.” You can also click on the “Choose from the most-used tags” link to see all of the tags used by the site.
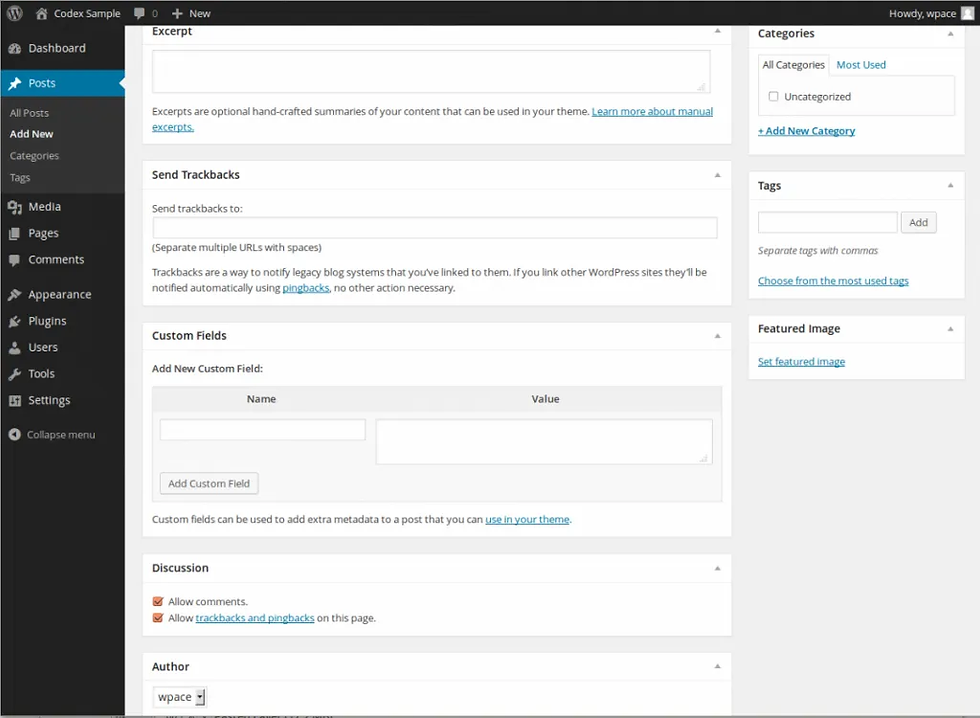
8. Excerpt
A summary or brief teaser of your post that may appear on the front page of your site as well as on the category, archives, and search non-single post pages. Note: the Excerpt does not usually appear by default. It only appears in your post if you have modified the template file listing the post to use the_excerpt() instead of the_content() to display the Excerpt instead of the full content of a post. If so, WordPress will automatically use as the Excerpt the first 55 words of your post content or the content before the <!–more–> quicktag. If you use the “Excerpt” field when editing the post, this will be used no matter what. For more information, see Excerpt.
9. Send Trackbacks
A way to notify legacy blog systems that you’ve linked to them. If you link other WordPress blogs, they’ll be notified automatically using pingbacks. No other action is necessary. For those blogs that don’t recognize pingbacks, you can send a trackback to the blog by entering the website address(es) in this box, separating each one by a space. See Trackbacks and Pingbacks for more information.
10. Custom Fields
Custom Fields offer a way to add information to your site. In conjunction with extra code in your template files or plugins, Custom Fields can modify the way a post is displayed. These are primarily used by plugins, but you can manually edit that information in this section.
11. Discussion
Options to enable interactivity and notification of your posts. This section hosts two check boxes: Allow Comments on this post and Allow trackbacks and pingbacks on this post. If Allowing Comments is unchecked, no one can post comments to this particular post. If Allowing Pings is unchecked, no one can post pingbacks or trackbacks to this particular post.
12. Post Author
A list of all blog authors you can select from to attribute as the post author. This section only shows if you have multiple users with authoring rights in your blog. To view your list of users, see Administration Screens > Users. For more information, see Users and Authors.
Note: You can set basic options for writing, such as the size of the post box, how smiley tags are converted, and other details by going to Administration Screens > Settings > Writing.
Practices For Posting:
You can say or show the world anything you like on your WordPress site. Here are some tips you need to know to help you write your posts in WordPress.
1. Practice Accessibility
To be compliant with web standards for accessibility, be sure to include ALT and TITLE descriptions on links and images to help your users, such as
<a title=”WordPress.ORG” href=”https://wordpress.org/“>WordPress.ORG</a>.2. Use Paragraphs
No one likes to read writing that never pauses for a line break. To break your writing up into paragraphs, use double spaces between your paragraphs. WordPress will automatically detect these and insert <p> HTML paragraph tags into your writing.
3. Use Headings
If you are writing long posts, break up the sections by using headings, small titles to highlight a change of subject. In HTML, headings are set by the use of h1, h2, h3, h4, and so on.
4. Use HTML
You don’t have to use HTML when writing your posts. WordPress will automatically add it to your site, but if you do want control over different elements like boxes, headings, and other additional containers or elements, use HTML.
5. Spell Check and Proofread
There are spell check Plugins available, but even those can’t check for everything. Some serious writers will write their posts in a text editor with spell check, check all the spelling and proof it thoroughly before copying and pasting into WordPress.
The Tech Platform

Comments